1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
|
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
BATCH_SIZE = 30
seed = 2
rdm = np.random.RandomState(seed)
X = rdm.randn(300,2)
Y_ = [int(x0*x0 + x1*x1 <2) for (x0,x1) in X]
Y_c = [['red' if y else 'blue'] for y in Y_]
X = np.vstack(X).reshape(-1,2)
Y_ = np.vstack(Y_).reshape(-1,1)
print( X)
print( Y_)
print( Y_c)
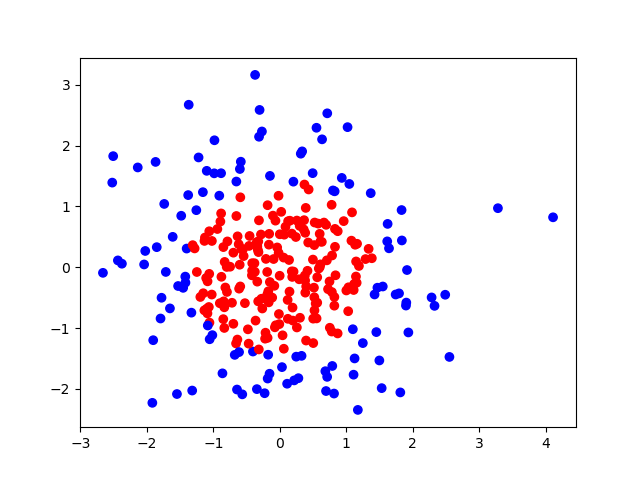
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=np.squeeze(Y_c))
plt.show()
def get_weight(shape, regularizer):
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape), dtype=tf.float32)
tf.add_to_collection('losses', tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(regularizer)(w))
return w
def get_bias(shape):
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.01, shape=shape))
return b
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 2))
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 1))
w1 = get_weight([2,11], 0.01)
b1 = get_bias([11])
y1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, w1)+b1)
w2 = get_weight([11,1], 0.01)
b2 = get_bias([1])
y = tf.matmul(y1, w2)+b2
loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_))
loss_total = loss_mse + tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(loss_mse)
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
STEPS = 40000
for i in range(STEPS):
start = (i*BATCH_SIZE) % 300
end = start + BATCH_SIZE
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:X[start:end], y_:Y_[start:end]})
if i % 2000 == 0:
loss_mse_v = sess.run(loss_mse, feed_dict={x:X, y_:Y_})
print(("After %d steps, loss is: %f" %(i, loss_mse_v)))
xx, yy = np.mgrid[-3:3:.01, -3:3:.01]
grid = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
probs = sess.run(y, feed_dict={x:grid})
probs = probs.reshape(xx.shape)
print( "w1:\n",sess.run(w1))
print( "b1:\n",sess.run(b1))
print( "w2:\n",sess.run(w2))
print( "b2:\n",sess.run(b2))
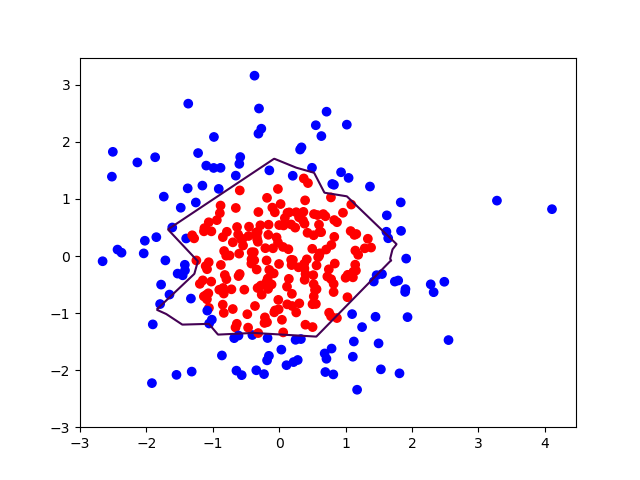
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=np.squeeze(Y_c))
plt.contour(xx, yy, probs, levels=[.5])
plt.show()
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(loss_total)
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
STEPS = 40000
for i in range(STEPS):
start = (i*BATCH_SIZE) % 300
end = start + BATCH_SIZE
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: X[start:end], y_:Y_[start:end]})
if i % 2000 == 0:
loss_v = sess.run(loss_total, feed_dict={x:X,y_:Y_})
print(("After %d steps, loss is: %f" %(i, loss_v)))
xx, yy = np.mgrid[-3:3:.01, -3:3:.01]
grid = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
probs = sess.run(y, feed_dict={x:grid})
probs = probs.reshape(xx.shape)
print( "w1:\n",sess.run(w1))
print( "b1:\n",sess.run(b1))
print( "w2:\n",sess.run(w2))
print( "b2:\n",sess.run(b2))
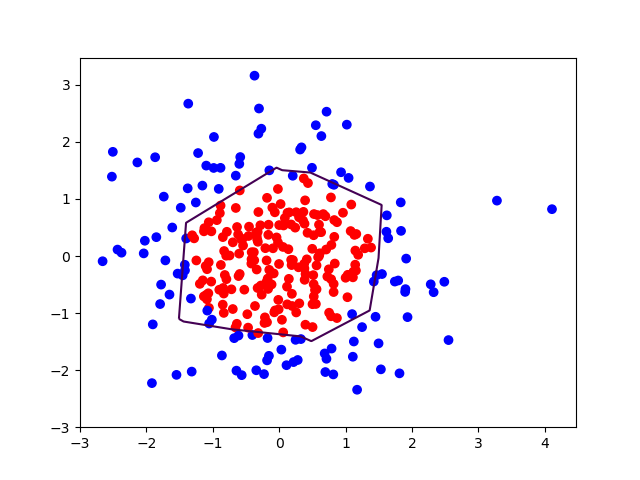
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=np.squeeze(Y_c))
plt.contour(xx, yy, probs, levels=[.5])
plt.show()
|